Configure a Project
You can configure additional settings for your projects, including the project name, directory, etc. Some of these settings are optional while others may be mandatory depending on how your Git repository has been set up.
To configure a project's settings , open the 3-dot menu for the project and
click on Settings.
Project name
To change the project name, enter the new name for your project as shown below.
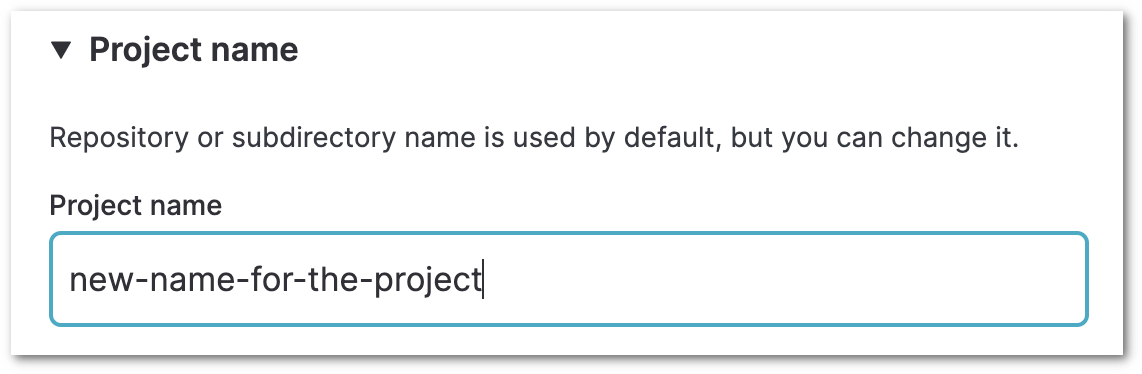
Project directory
If the DVC repo for which you are creating the project is not in the root of your Git repository but is in a sub-directory of a monorepo, then specify the full path to the sub-directory that contains the DVC repo to which you are trying to connect.
Create multiple projects at once by providing up to 10 comma-separated values during the initial create project flow.
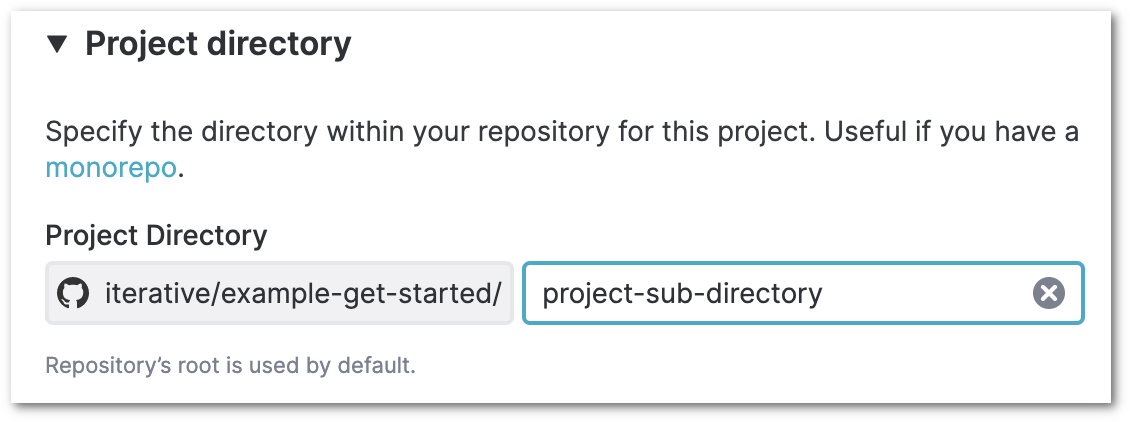
Data remotes / cloud storage credentials
Here, the data remotes (cloud storage or another location outside the Git repo) that are used in your DVC repo will be listed. If you want your project to include data stored in these data remotes, you will have to add credentials to grant DVC Studio access to the data remotes. Credentials that you have already added to your account are listed in this section, and you can select them to add them to the project.
To add new credentials, click on Add new credentials and select the provider
(Amazon S3, GCP, etc.). For details on what types of remote storage (protocols)
are supported, refer to the DVC documentation on supported storage types.
Depending on the provider, you will be asked for more details such as the credentials name, username, password etc. Note that for each supported storage type, the required details may be different.
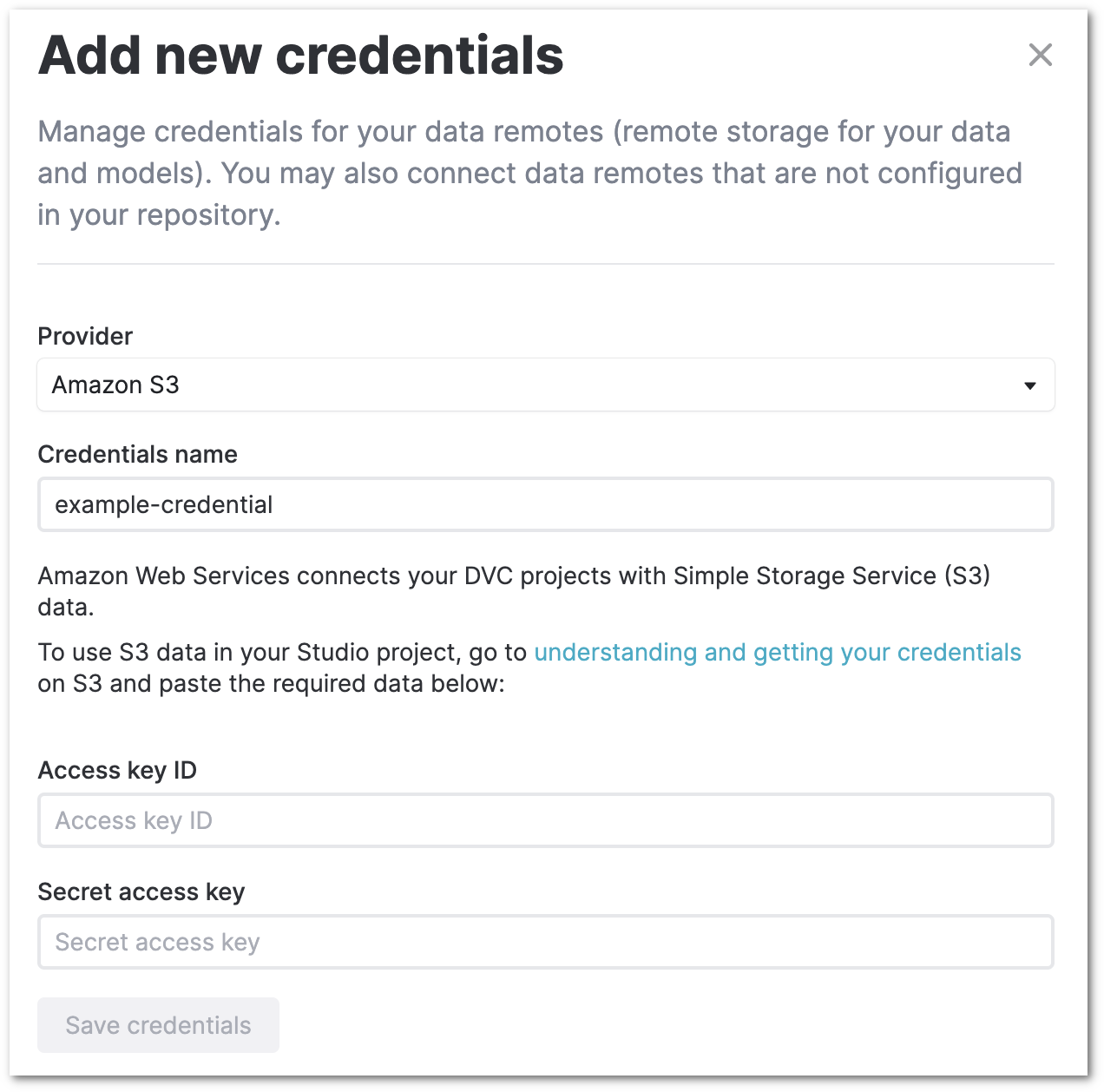
You will also have to ensure that the credentials you enter have the required permissions on the cloud / remote storage. Refer to the DVC Remote config parameters for more details about this.
Any credentials that you add in your profile page are also available in your project settings page.
Note that DVC Studio uses the credentials only to read plots/metrics files if they are not saved in Git. It does not access any other data in your remote storage. And you do not need to provide the credentials if any DVC data remote is not used in your Git repository.
Commits and columns
You can specify which Git commits and columns should be imported from your Git repository to your project in DVC Studio, and which ones should be excluded.
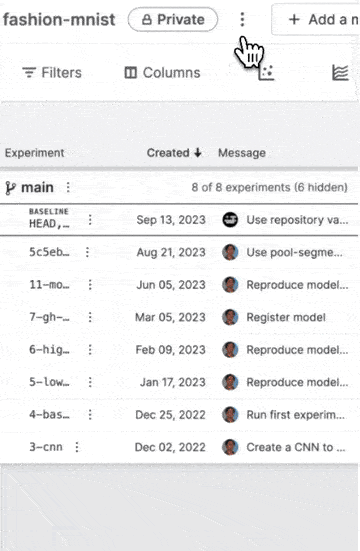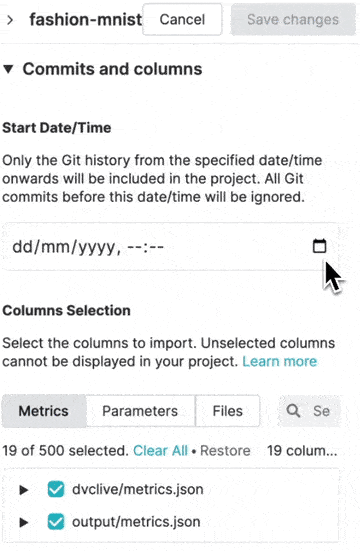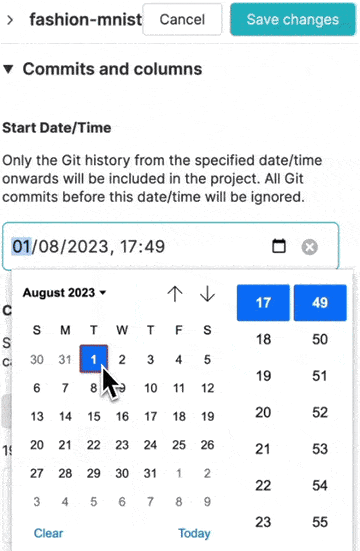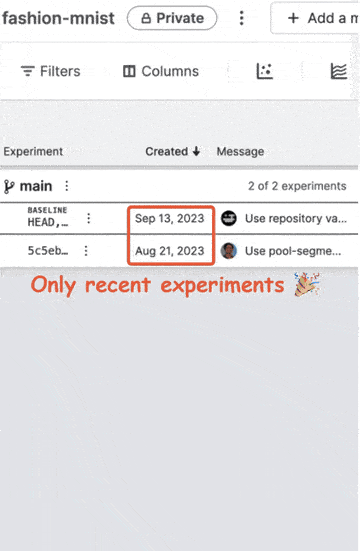
Start date/time
If your Git history has old commits that are not relevant to your project anymore, you can set a cut-off date so that these outdated commits are not imported in your project. Your old commits will remain in your Git repository, but will not over-crowd your projects any more. This will let you focus on recent experiments, metrics and plots.
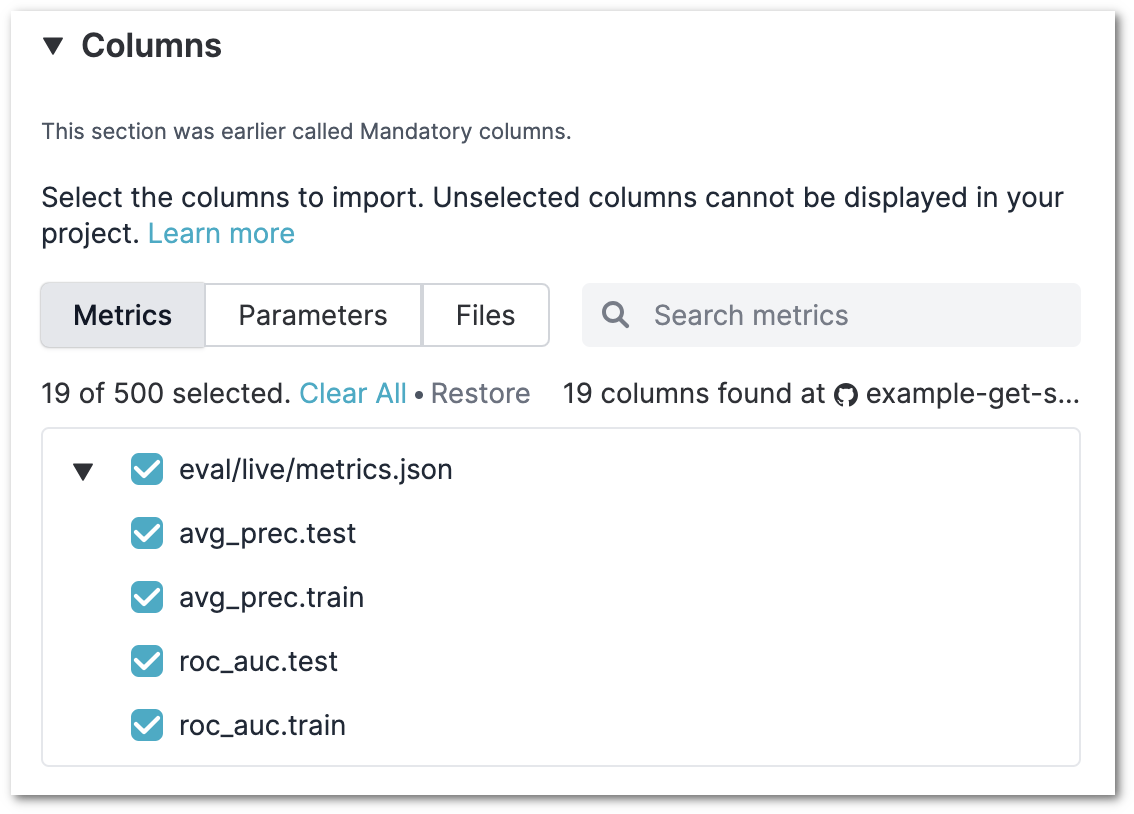
Columns
You can specify which columns should be imported from your Git repository to your project. Any unselected column cannot be displayed in your project table.
If you would like to hide imported columns from your project, you can do so in the project's Display preferences.
If your project is missing some required columns, then it is likely that they have not been imported or are hidden.
The Columns setting was earlier called Tracking scope or Mandatory columns and behaved slightly differently. DVC Studio would always import up to 200 columns. This meant that if you selected only 5 columns, DVC Studio would still import another 195 columns, unless your repository did not have so many columns. This behavior is now obsolete, and only selected columns are imported.