Sharing Experiments
See the video below for how to share experiments using the DVC Extension for VS Code, or keep reading to go deeper.
Share automatically
By default, your experiments are stored only where they were run. To automatically share all experiment info, you will need a:
- Git remote (for example, GitHub)
- DVC remote storage for any large artifacts you want DVC to track
- DVC Studio project connected to that Git remote
To automatically share your experiments, run:
$ dvc studio loginOnce configured, DVC will:
- send live metrics and plots to DVC Studio
- push experiment code and metadata to your Git repo
- push data, models, and other artifacts to your DVC remote storage
Keep reading for how to granularly control what information gets shared and when.
Live metrics and plots
dvc studio login will set your access token to automatically send live
metrics and plots.
You can send live experiments to DVC Studio, which will show intermediate results for metrics and plots in any running experiments. To start sharing live metrics to DVC Studio, set your access token.
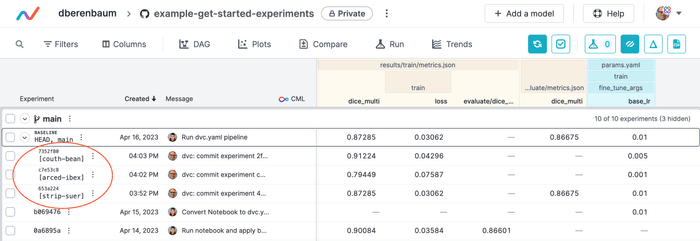
While the experiment runs, you will see live updates like this in DVC Studio (and so will anyone else with access to the project):
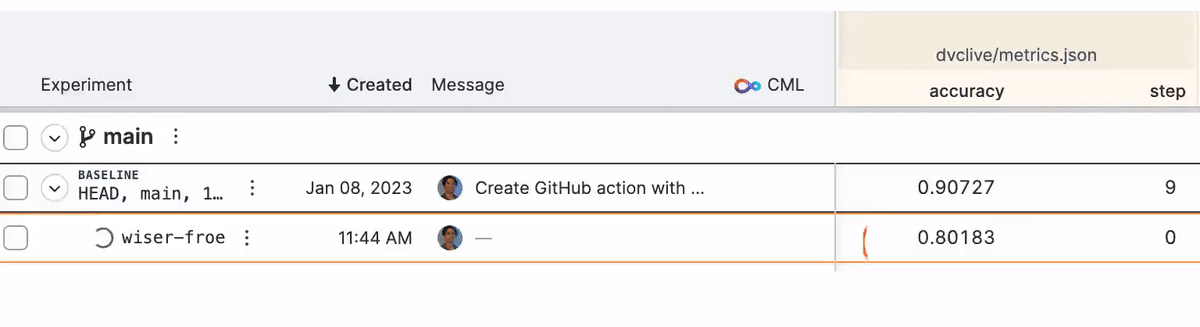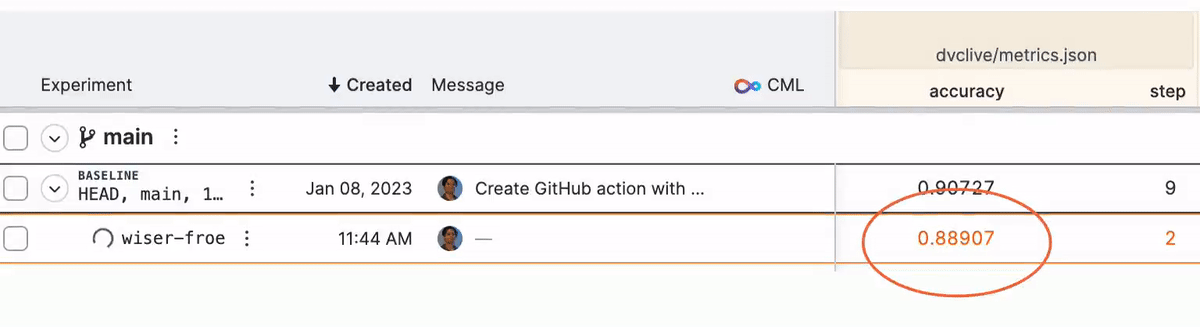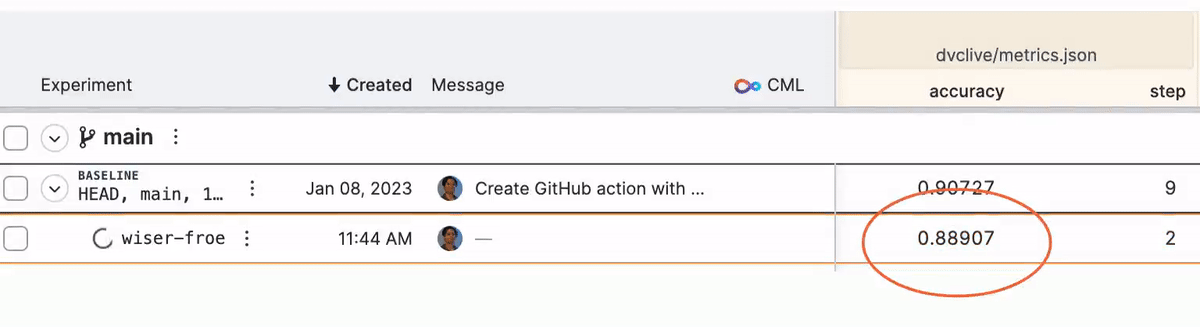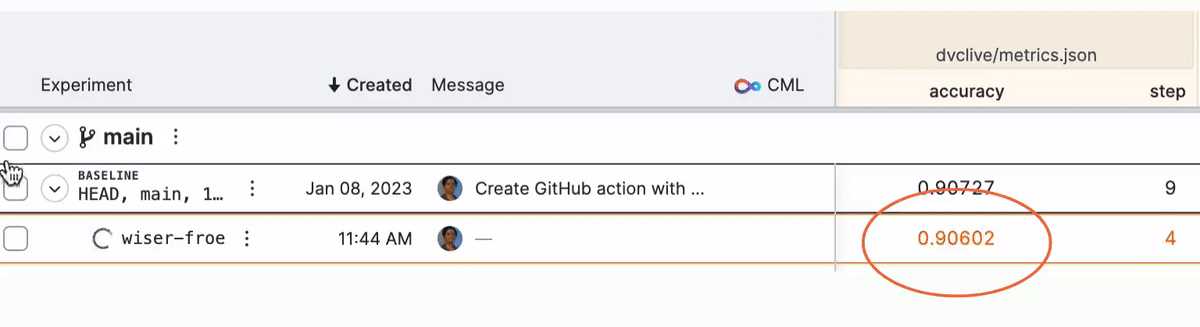
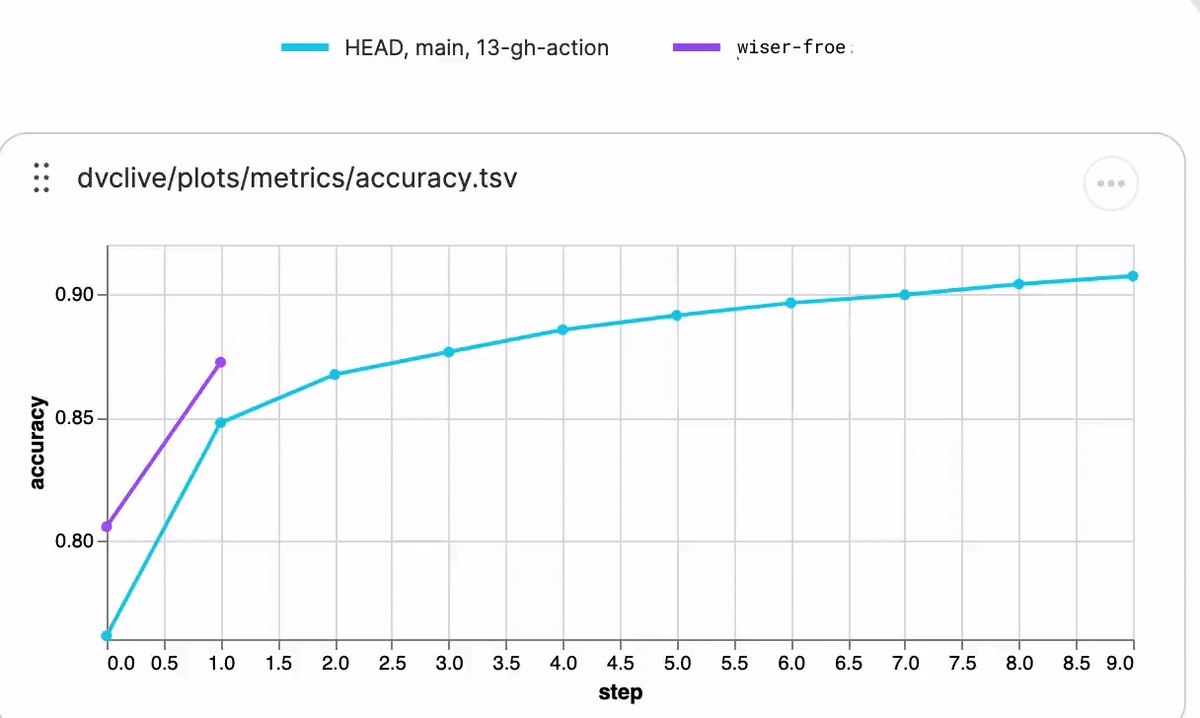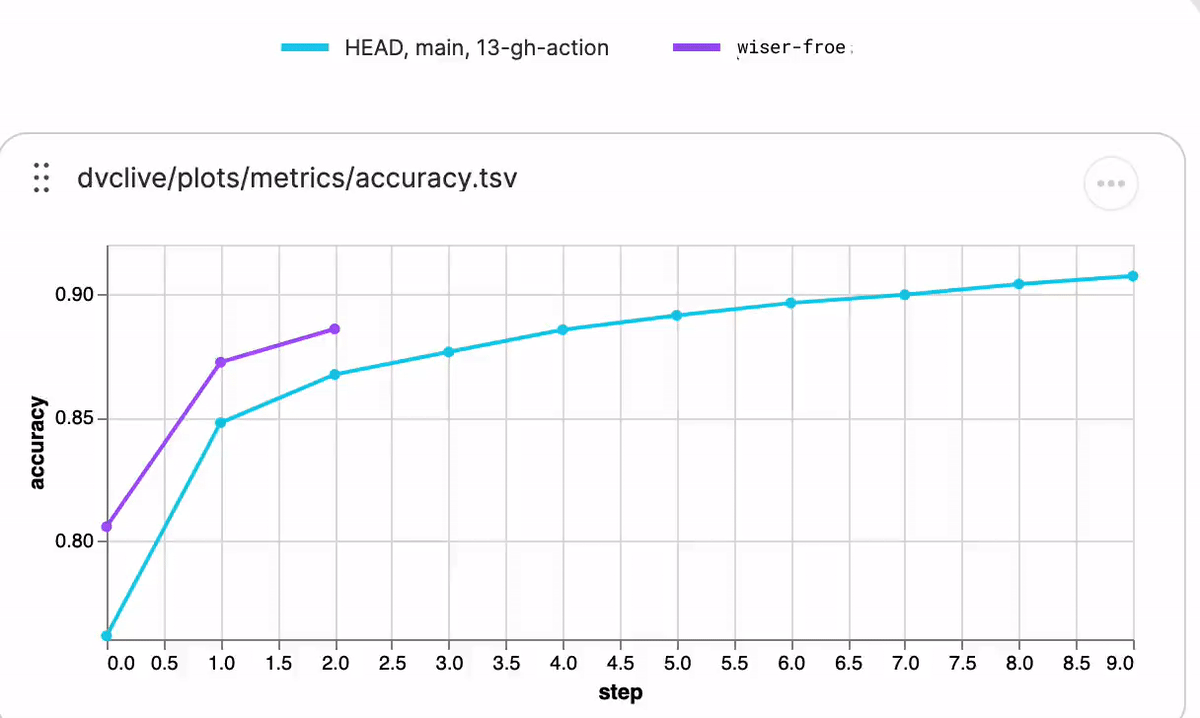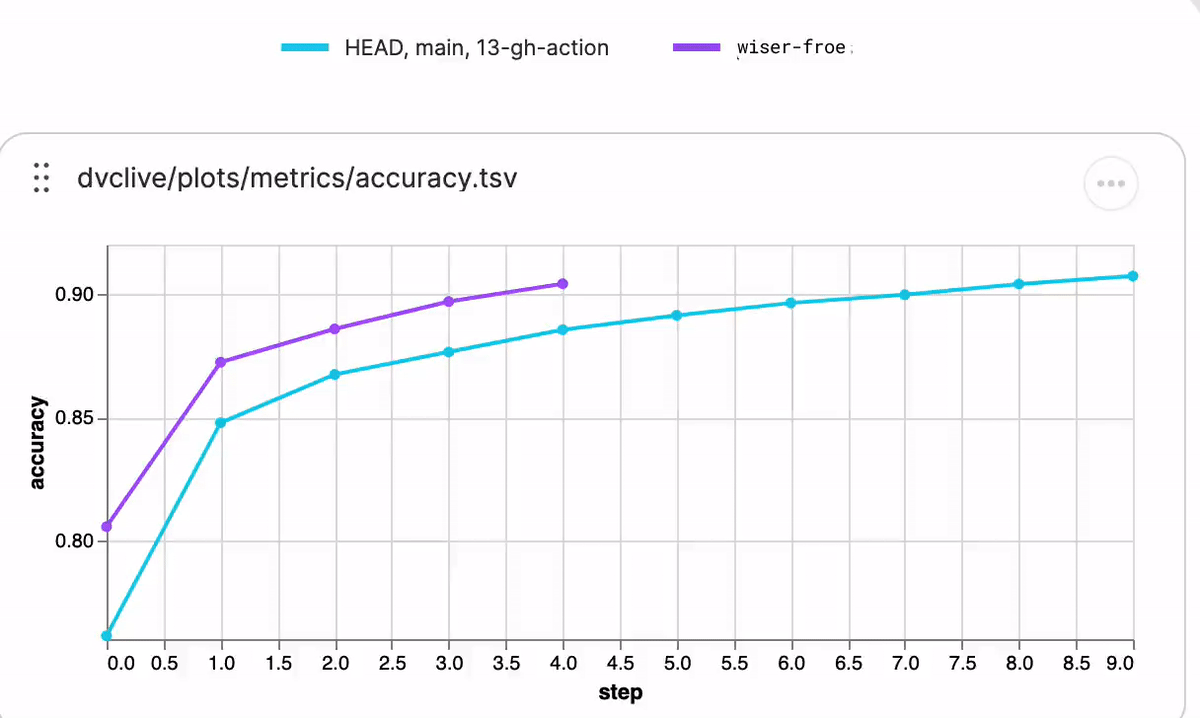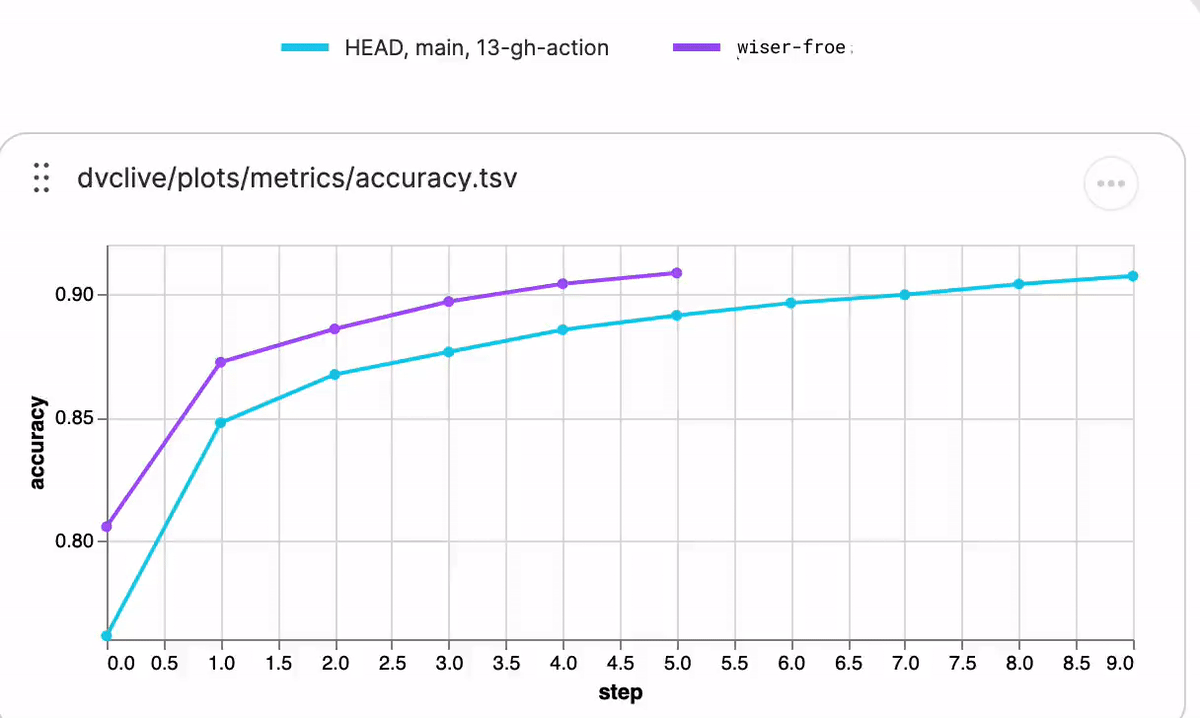
See DVC config for how to enable/disable live metrics and how to configure a different DVC Studio URL or Git repository, or see the DVC Studio guide on [live experiments] for more information on how to setup, view, and compare.
Push experiments
dvc studio login will configure DVC to
push experiments automatically.
dvc exp push pushes experiment commits that Git can upload to
remote servers like GitHub but don't show up in the UI (so they don't clutter
your repo) and can be cleaned up without affecting the rest of your project.
To understand how dvc exp push works, let's compare to pushing a persistent
commit. With a typical Git commit, you would use git push to upload it to your
Git remote and dvc push to upload the corresponding data to your DVC remote.
┌────────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐
├────────────────┤ │ DVC remote │ Remote locations
│ Git remote │ │ storage │
│ │ ├────────────────┤
└────────────────┘ └────────────────┘
▲ ▲
│ │
git push dvc push
git pull dvc pull
│ │
▼ ▼
┌────────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐
│ Code and │ │ Data │
│ metafiles │ │ (cached) │ Local project
└────────────────┘ └────────────────┘dvc exp push and dvc exp pull take care of synchronizing to/from both Git
and DVC remotes as needed:
┌────────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐
├────────────────┤ │ DVC remote │ Remote locations
│ Git remote │ │ storage │
│ │ ├────────────────┤
└────────────────┘ └────────────────┘
▲ ▲
│ dvc exp push │
│ dvc exp pull │
▼ ▼
┌─────────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐
│ Code and │ │ Data │
│ metafiles │ │ (cached) │ Local project
└─────────────────┘ └────────────────┘DVC experiments are tied to your Git repo, but they are ignored by
normal Git operations like git push, git pull, and git clone. You can
upload completed experiments using dvc exp push. This will push not only
metrics and plots, but also the code and DVC-cached files (data and
models) so you can pull an experiment, make it persistent, and reproduce it
from your Git repo. For example, in the simplest case, push experiments to Git
remote origin:
$ dvc exp push originIf you don't know your Git remote, check with git remote -v or see
troubleshooting for problems.
By default, DVC will also share cached data that is tracked by DVC,
which requires remote storage (e.g. Amazon S3 or SSH). Add the --no-cache
flag to exclude sharing cached data.
By default, dvc exp push origin will push all experiments derived from your
current Git commit, but you may specify specific experiments as arguments or use
the flags to select a different set of experiments to push.
To push the experiment automatically at the end of a dvc exp run or
dvc exp save set the configuration option exp.auto_push to true:
$ dvc config exp.auto_push trueor use the environment variable DVC_EXP_AUTO_PUSH.
By default, the experiments will be pushed to the remote origin. To change the
default value, set the configuration option exp.git_remote or the
environment variable DVC_EXP_GIT_REMOTE.
Find pushed experiments
You can see pushed experiments in DVC Studio. From there, you can make an experiment persistent by creating a Git branch, or you can remove it from your Git remote:
From your workspace, you can see pushed experiments if you provide a Git remote
name to dvc exp list.
$ dvc exp list origin
refs/tags/baseline-experiment:
cnn-32
cnn-64dvc exp list origin lists remote experiments based on your current commit. You
can use --all-commits (-A) to list all experiments, or add any other
supported option.
Pull experiments
To download pushed experiments, use dvc exp pull (with the Git remote and
experiment name).
$ dvc exp pull originThis puts all the necessary files and data (from both Git and DVC remotes) in your project.
Add the --no-cache flag to exclude pulling from the DVC remote.
By default, dvc exp pull origin will pull all experiments derived from your
current Git commit, but you may specify specific experiments as arguments or use
the flags to select a different set of experiments to push.
Persist experiment
DVC experiments run outside of the regular Git workflow for faster iteration and to avoid polluting your repository's history, but you can easily bring back the most promising experiments into your regular Git workflow. You can convert any pushed experiment from DVC Studio into a persistent Git branch and create a pull request to merge it into your main repo branch:
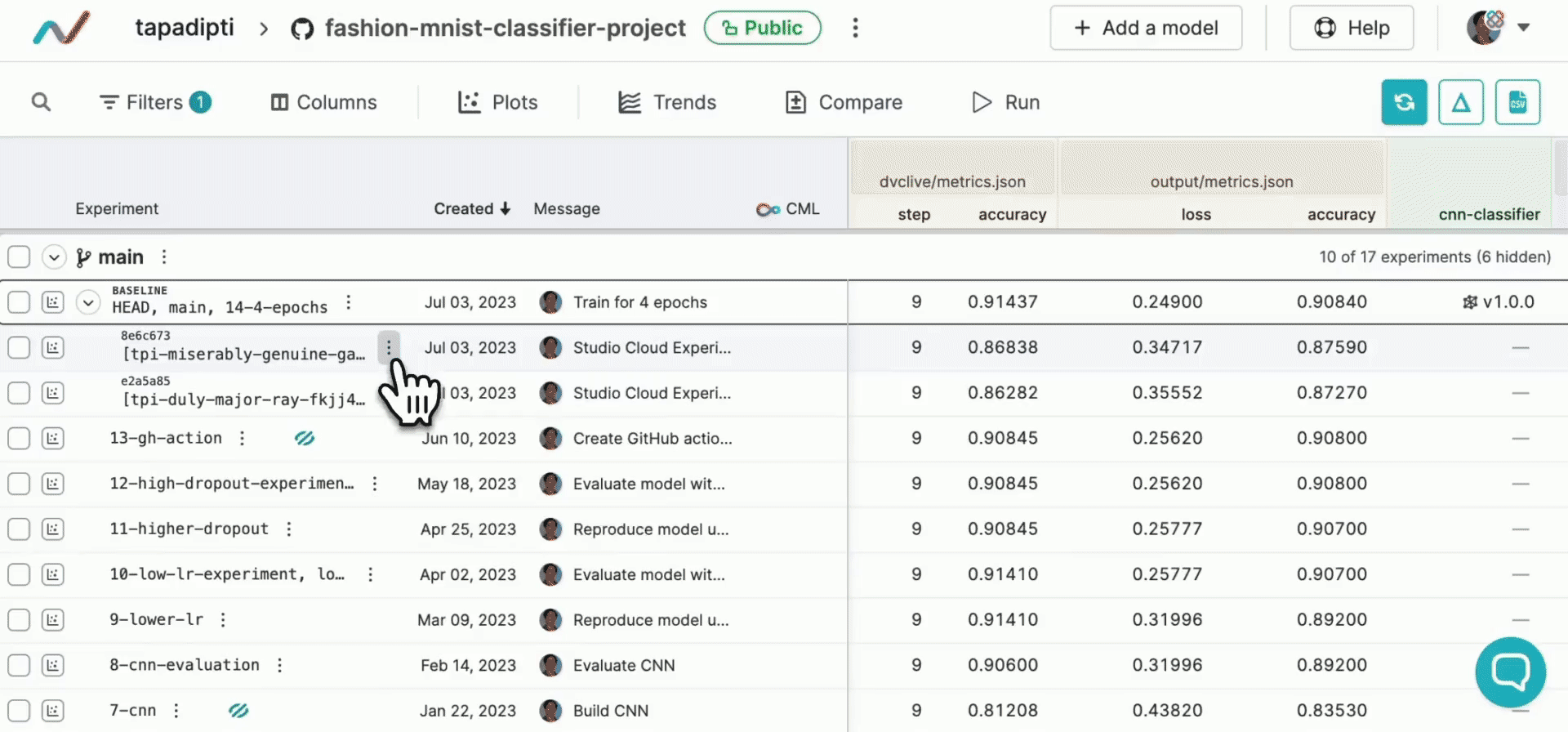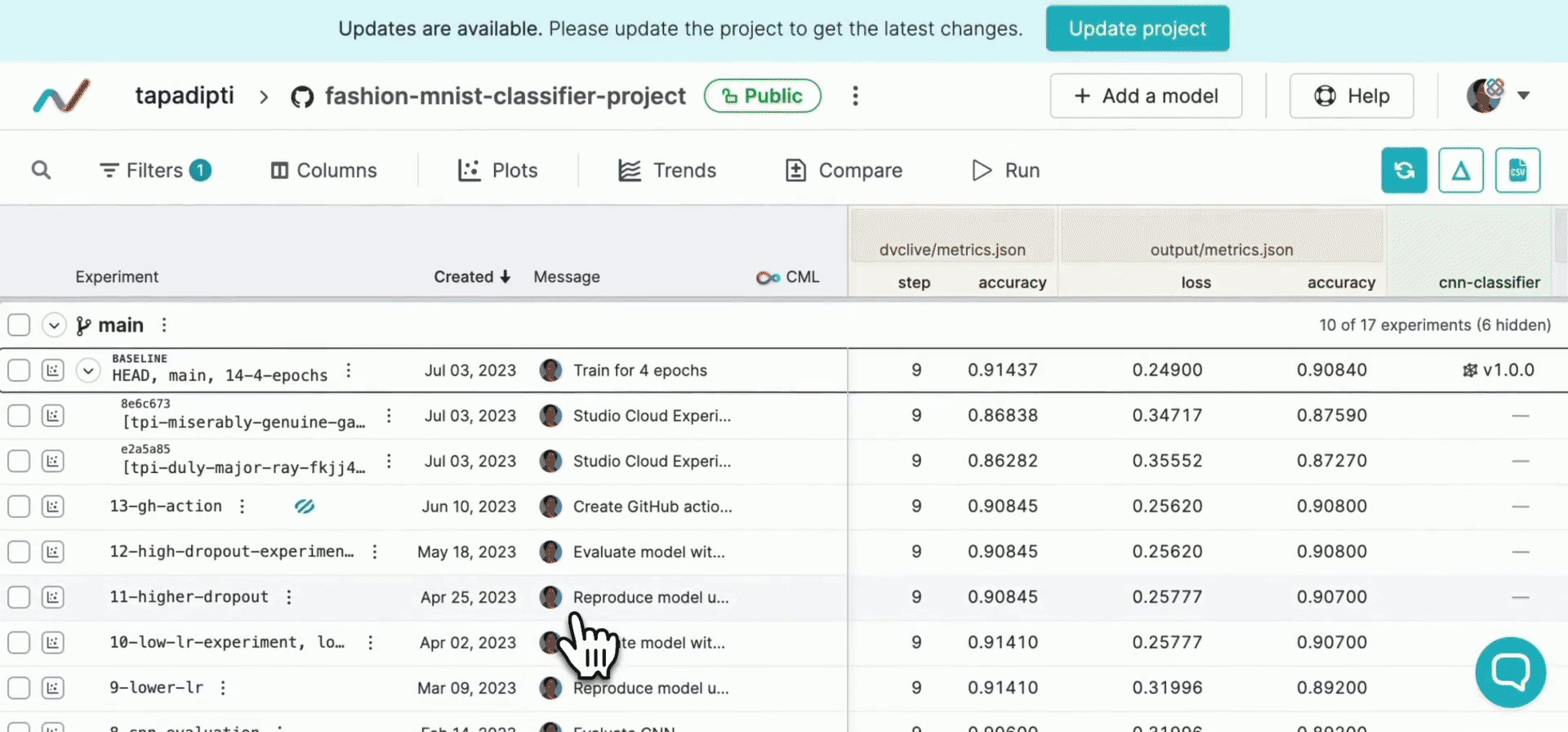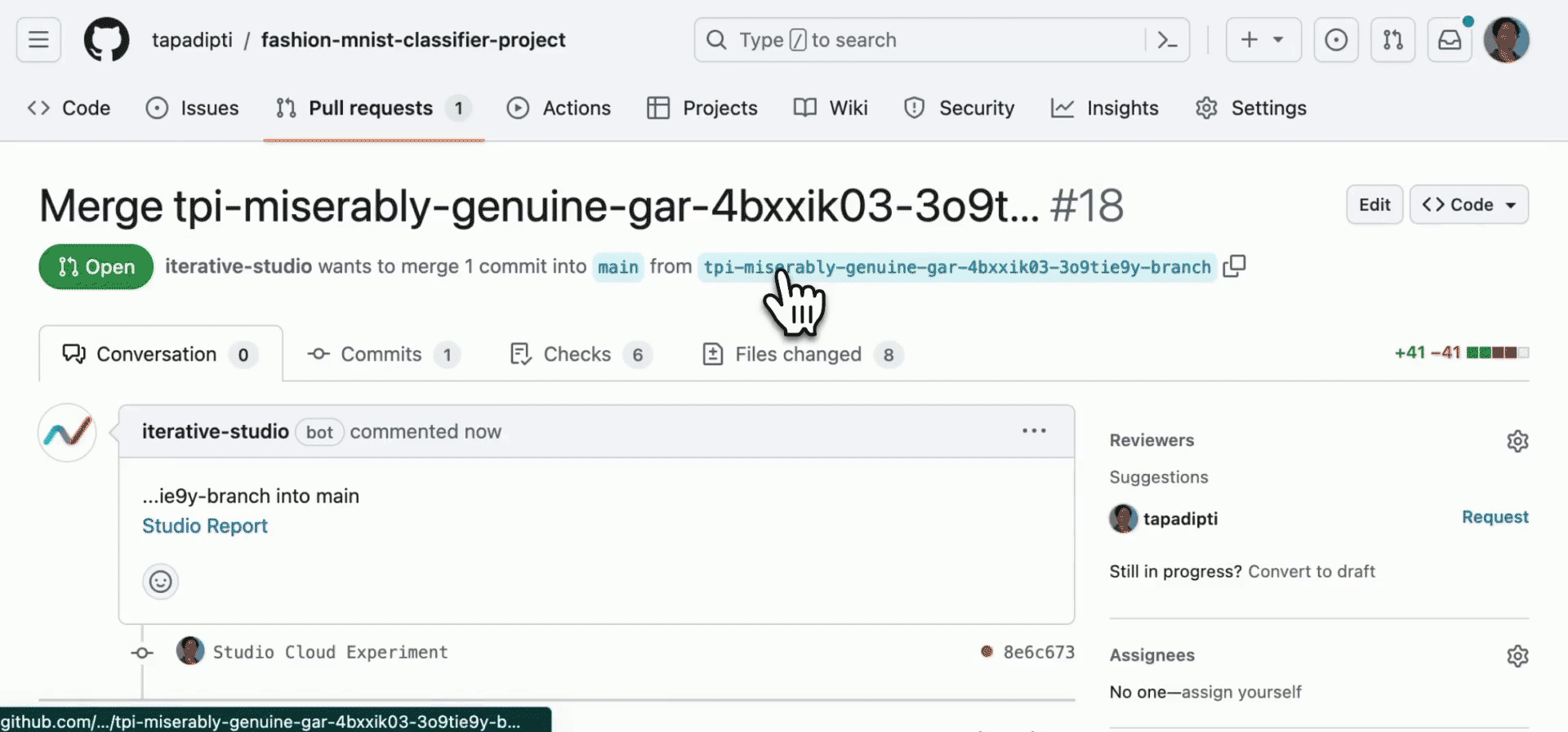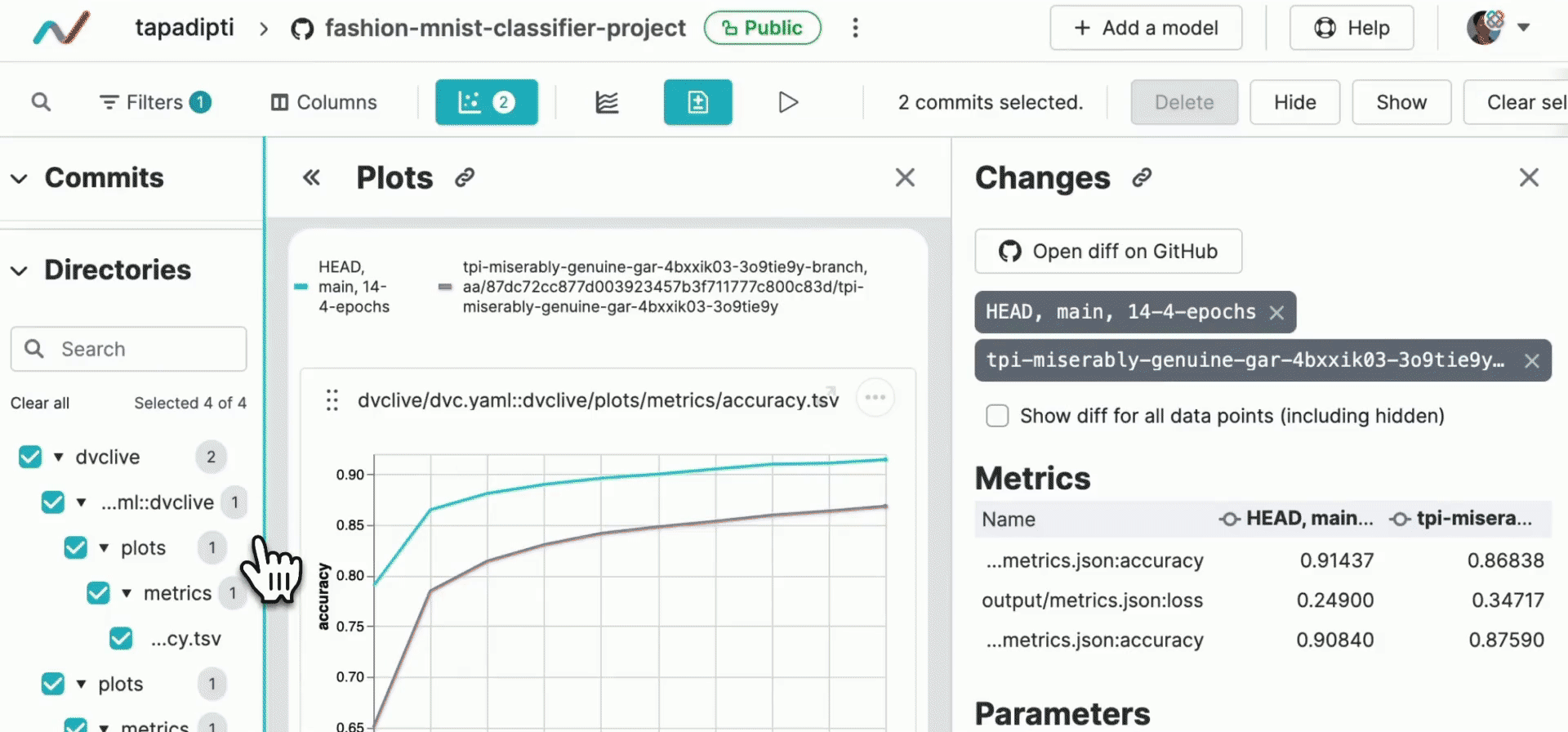
Alternatively, from your workspace, to share an individual experiment the same
way you share other Git commits, use dvc exp branch to create
a Git branch from the experiment and share it like any Git
branch.
$ dvc exp branch quare-zips
Git branch 'quare-zips-branch' has been created from experiment 'quare-zips'.
$ git checkout quare-zips-branch
Switched to branch 'quare-zips-branch'
$ git push origin quare-zips-branchIf you only need to share code and metadata (like parameters and metrics), then pushing to Git should be enough.
You may also have cached data, models, etc. tracked by DVC. To
share these, dvc push them to remote storage (e.g. Google Drive or NAS).
$ dvc pushIf you don't want to create a new Git branch and instead want to commit the experiment directly on top of your current Git branch, you can bring experiment results to your workspace.
Remove pushed experiments
As you share more experiments, DVC Studio and Git remotes may be become cluttered with experiment references.
You can remove experiments in DVC Studio:
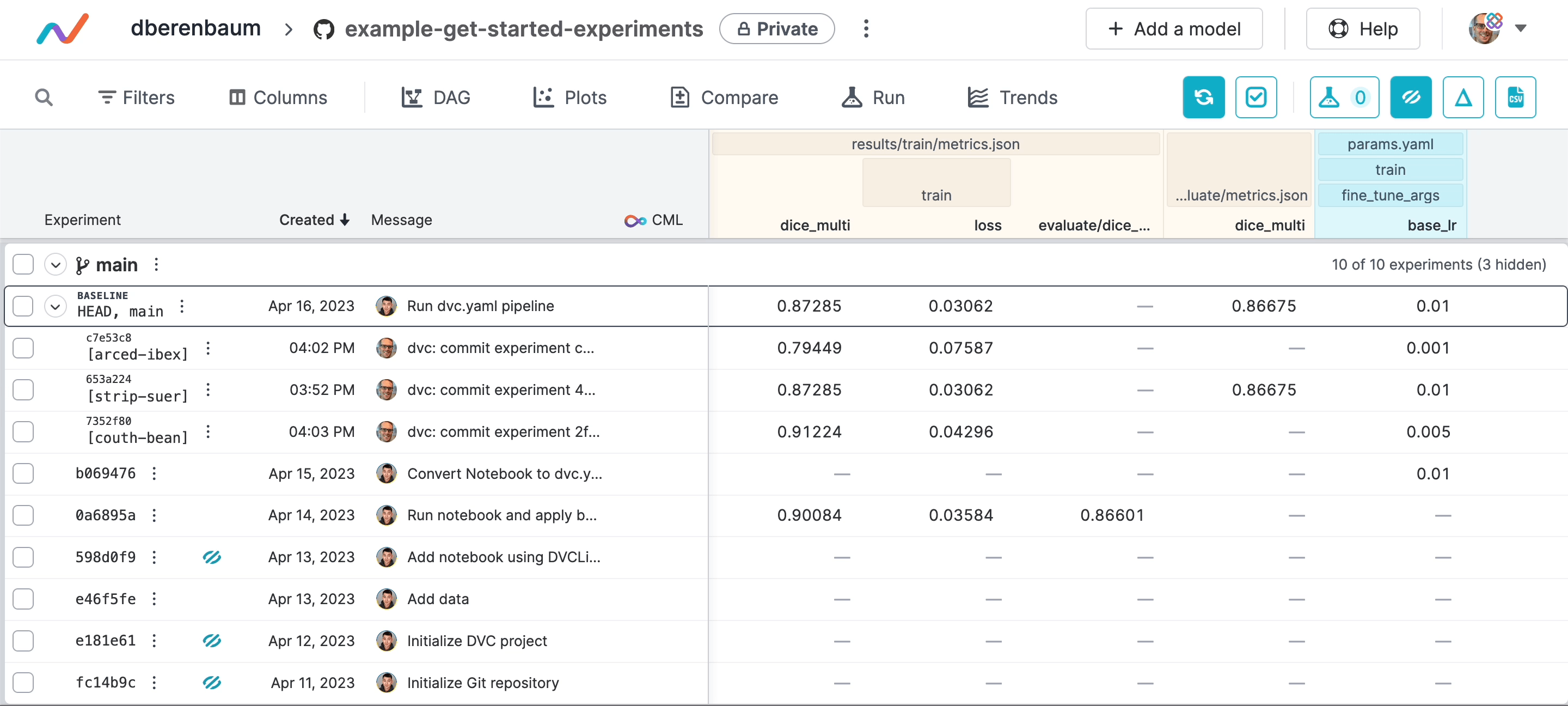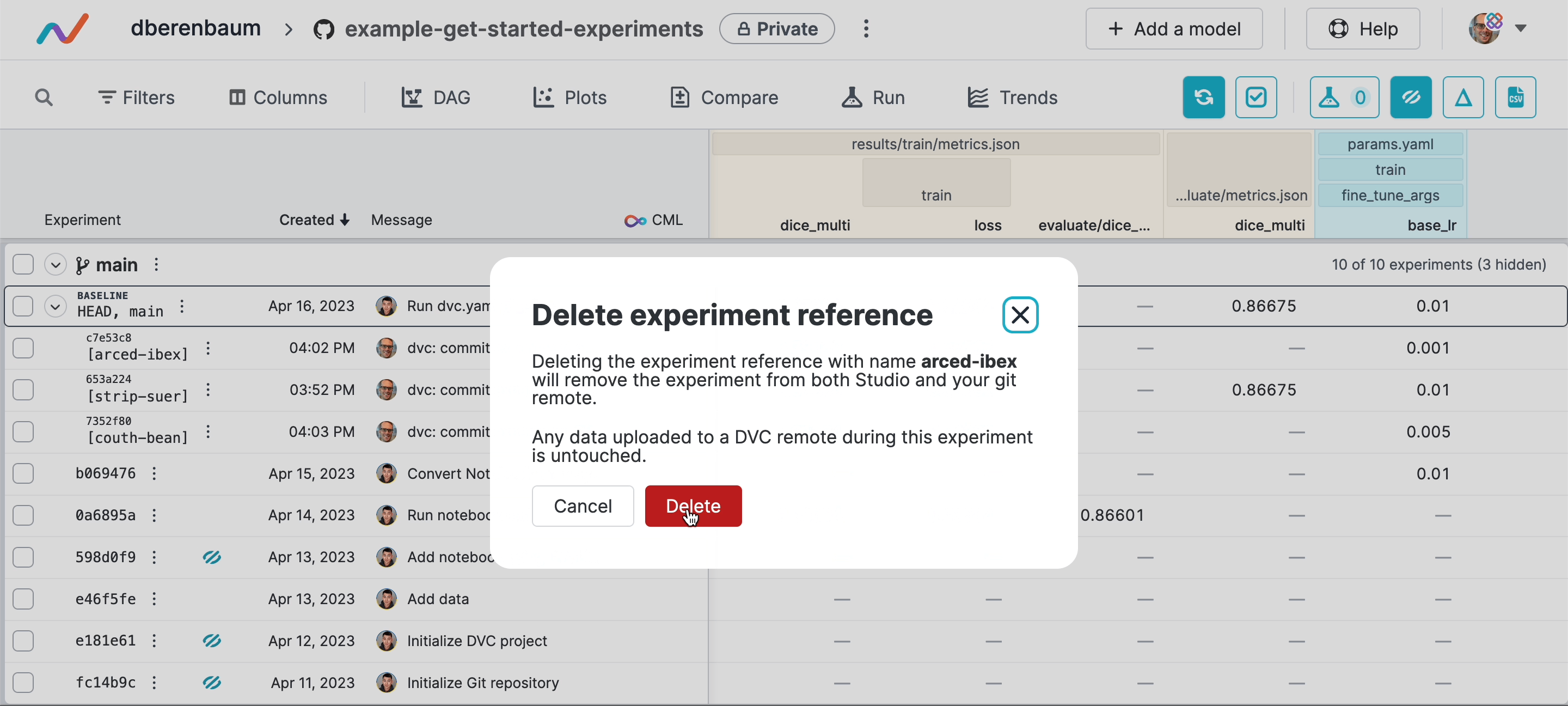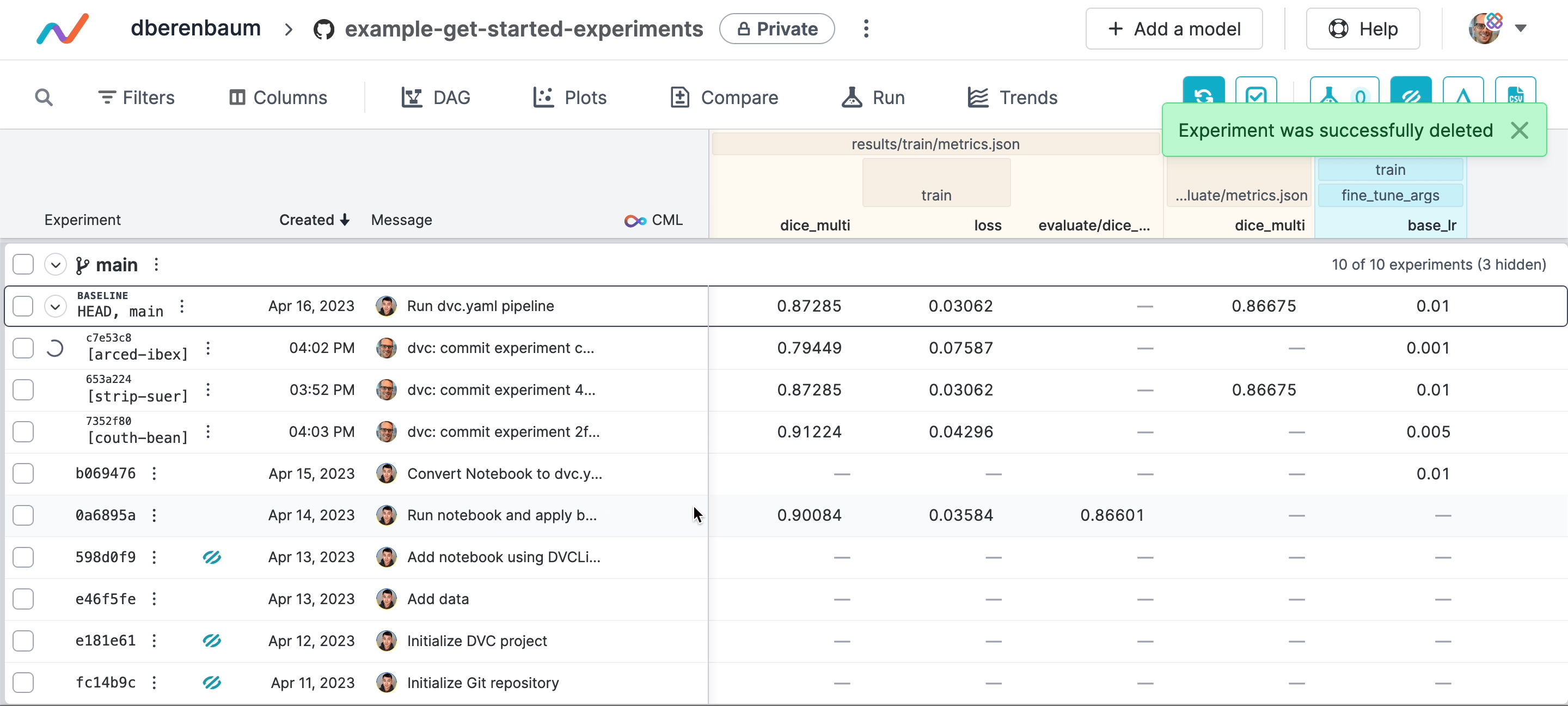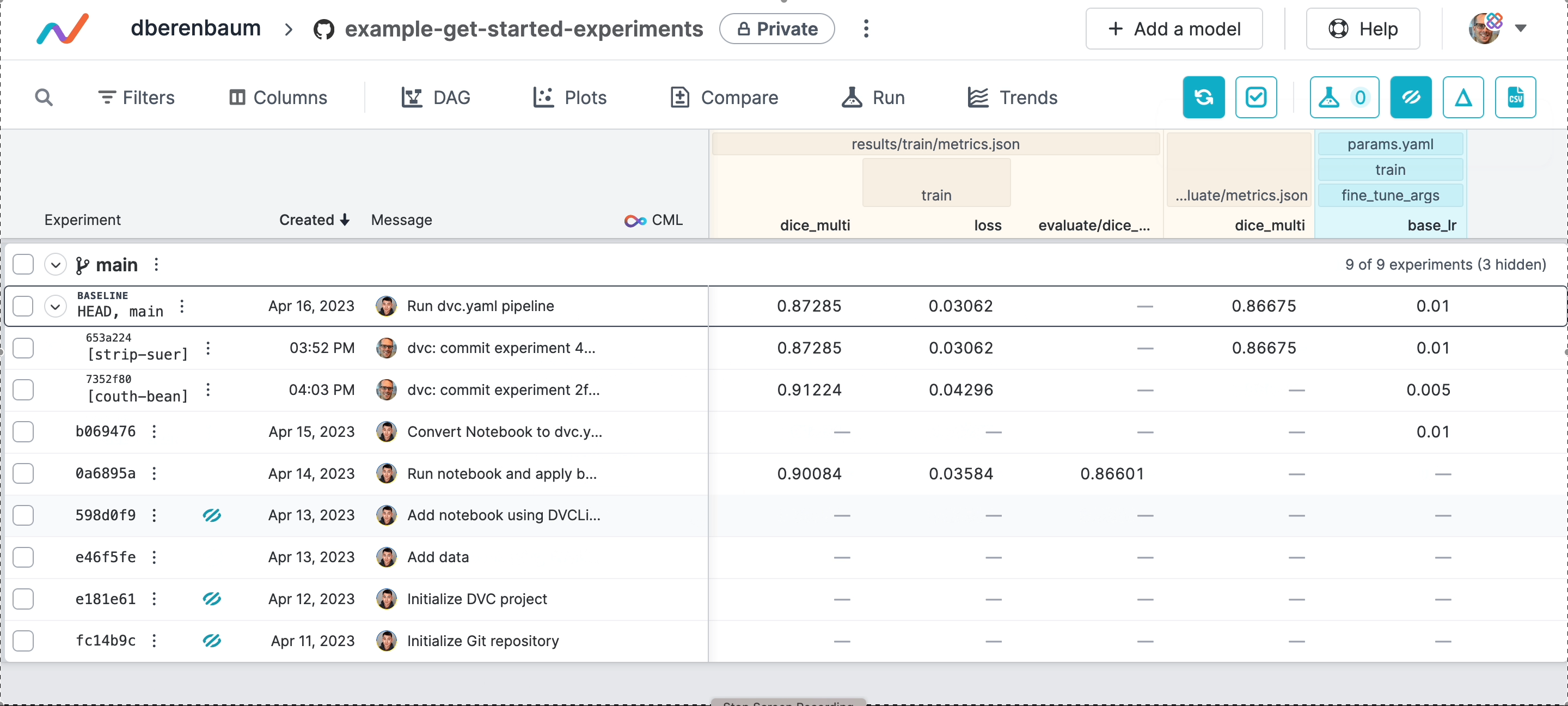
To remove pushed experiments using the command line, use dvc exp remove -g:
$ dvc exp remove -g origin unwet-jinn
Removed experiments: unwet-jinn